Help is here
What is a Tire Monitor Sensor and How Does It Work?
A tire monitor sensor is a vital component in modern vehicles, designed to enhance safety and improve overall driving performance. By continuously measuring the air pressure within each tire, this sensor plays a crucial role in preventing tire-related incidents, ensuring that drivers are promptly alerted to any potential issues. The technology behind tire monitor sensors has advanced significantly, allowing for real-time data transmission to the vehicle’s onboard system, which in turn keeps the driver informed about tire conditions.
Understanding how tire monitor sensors work is essential for both drivers and automotive enthusiasts. These sensors are typically mounted inside or outside the tire and communicate directly with the vehicle's computer system. When the tire pressure drops below a certain threshold, the sensor detects this change and triggers a warning indicator on the dashboard. This early detection allows drivers to take proactive measures, such as inflating the tire or seeking professional assistance, ultimately enhancing road safety and extending tire lifespan.
In summary, tire monitor sensors represent a significant leap in automotive technology, reflecting the industry’s ongoing commitment to safety and efficiency. By exploring their functionality and importance, we can appreciate how these small yet powerful devices contribute to a more secure driving experience.
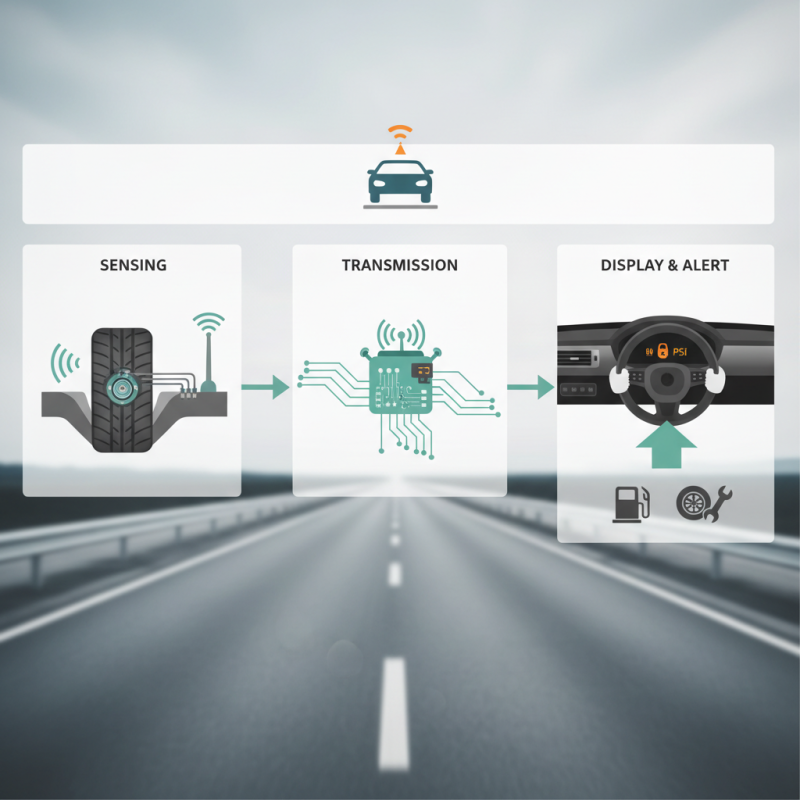
What is a Tire Monitor Sensor?
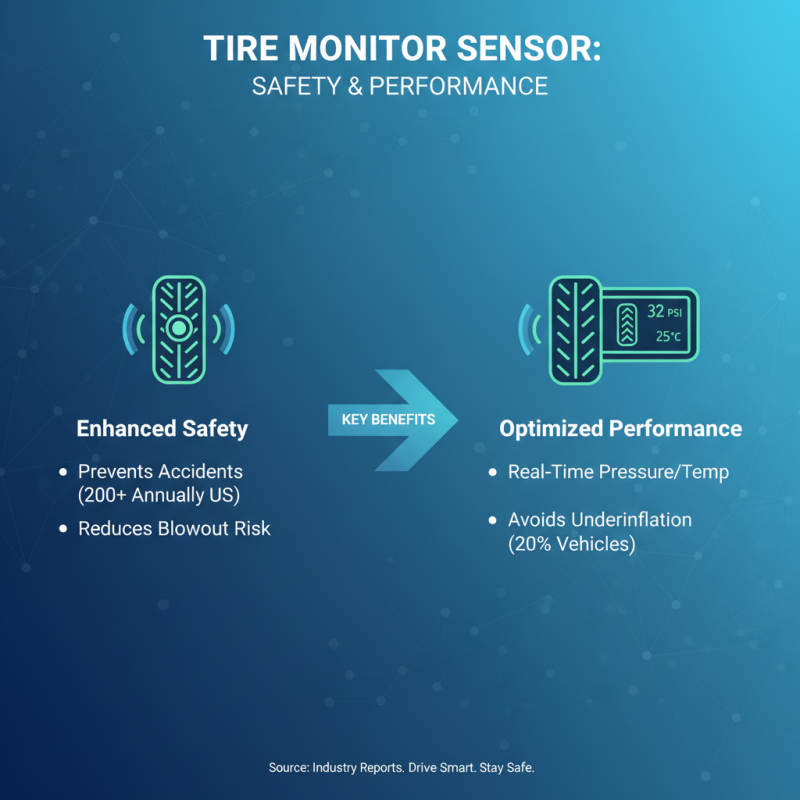
A tire monitor sensor is an essential component in modern vehicles, designed to enhance safety and optimize tire performance. These sensors are primarily responsible for continuously monitoring tire pressure and temperature, providing real-time data to the driver through the vehicle's dashboard. According to industry reports, approximately 20% of vehicles on the road have at least one tire significantly underinflated, leading to a higher risk of tire blowouts and accidents. The implementation of tire monitor sensors has significantly mitigated these risks, helping to prevent over 200 accidents annually in the United States alone.
The functionality of tire monitor sensors relies on two main types: direct and indirect systems. Direct tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) utilize sensors mounted on each tire to measure air pressure directly and transmit this data wirelessly to the vehicle's onboard computer. Conversely, indirect TPMS does not use dedicated sensors but instead analyzes the rotational speed of the tires through the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). By doing so, it can detect variations in tire inflation based on speed discrepancies. Recent data suggests that as of 2022, nearly 85% of new vehicles sold in North America are now equipped with direct TPMS technology, reflecting a growing trend toward enhanced vehicle safety features.
The Importance of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS)
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) play a crucial role in modern vehicle safety and performance. These systems help monitor and maintain optimal tire pressure, ensuring that vehicles operate efficiently and safely. By providing real-time data, TPMS alerts drivers to any significant deviations from the recommended tire pressure levels, which can be critical for preventing potential blowouts or loss of control while driving.
The importance of TPMS extends beyond mere convenience; it is a vital aspect of overall vehicle maintenance and safety. Proper tire pressure contributes to improved fuel efficiency, better handling, and extended tire life. Furthermore, maintaining the correct tire pressure reduces the risk of accidents caused by tire failure, thereby enhancing road safety for both drivers and pedestrians. As more vehicles come equipped with advanced TPMS technology, drivers are better equipped to make informed decisions regarding their tire health, ultimately leading to a safer driving experience.
How Tire Monitor Sensors Measure Pressure and Temperature
Tire monitor sensors are essential components of modern vehicles, particularly in ensuring optimal tire performance and safety. These sensors measure both tire pressure and temperature, providing real-time data that helps drivers maintain their vehicles more effectively. Understanding how tire monitor sensors function is key to appreciating their importance in automotive safety.
To measure tire pressure, the sensors utilize a piezoresistive element that detects the force exerted by the air within the tire. This element generates a voltage signal corresponding to the pressure level; a microcontroller then processes this signal and relays accurate pressure readings to the driver. For temperature measurement, the sensors often use thermistors, which change resistance based on temperature fluctuations. The sensor sends this data to the vehicle’s onboard computer, allowing for consistent monitoring and alerts in case of irregular conditions.
By continuously tracking both pressure and temperature, tire monitor sensors play a crucial role in preventing tire blowouts and improving fuel efficiency. When tires are optimally inflated and within designated temperature ranges, vehicles perform better and are safer on the road. These sensors represent a crucial advancement in vehicle technology, contributing to overall driving safety and convenience.
Types of Tire Monitor Sensors: Direct vs. Indirect Systems
Tire monitor sensors play a crucial role in maintaining vehicle safety by monitoring tire pressure and temperature. There are two primary types of tire monitoring systems: direct and indirect.
Direct systems involve sensors mounted directly on each tire, which measure real-time pressure and temperature data. These sensors transmit this information to the vehicle’s onboard computer system, allowing for precise monitoring and immediate alerts if tire conditions fall outside of safe parameters. This setup provides drivers with the most accurate information, essential for proactive vehicle maintenance.
On the other hand, indirect tire monitor systems do not use dedicated sensors for each tire. Instead, they rely on the vehicle's existing wheel speed sensors, which monitor the differences in rotational speed between tires. When a tire is under-inflated, it rolls at a different speed compared to properly inflated tires, triggering an alert in the vehicle's dashboard.
While this system is generally less expensive and easier to install, it does not provide real-time pressure readings and may be less effective at identifying gradual pressure losses. Understanding these differences is key for vehicle owners looking to enhance their tire maintenance strategies.
Troubleshooting Common Tire Monitor Sensor Issues
Tire Monitor Sensors (TMS) play a crucial role in vehicle safety by continuously monitoring tire pressure and temperature. However, issues can arise that affect their functionality. One common problem is the sensor battery running low. Typically, the lifespan of a tire monitor sensor battery is about 5-10 years, depending on usage conditions and environmental factors. When the battery weakens, it can result in inaccurate readings, leading to potential safety hazards. Drivers should regularly check their tire pressure and pay attention to warning lights on their dashboards to catch these issues early.
Another frequent issue involves faulty sensor calibration. Factors like tire rotation, replacement, or improper installation can cause the sensors to lose their calibration. According to a report from the Tire Industry Association, improper tire maintenance contributes to a significant percentage of tire-related accidents. To troubleshoot this, vehicle owners should refer to the owner's manual for re-calibration procedures or consult with a professional technician to ensure sensors are reading accurately.
Tips: Regularly inspect your tire monitor sensor system, especially after tire changes or rotations, and replace the sensors roughly every 5 years to maintain optimal performance. Additionally, it's wise to invest in a professional diagnostic when experiencing persistent issues to prevent further complications and enhance safety on the road.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Impact of Tire Valve Sensors on Vehicle Safety and Fuel Efficiency
-

Understanding the Importance of Tire Monitor Sensors for Safe Driving
-

Understanding Tire TPMS: How Your Car's Pressure Monitoring System Enhances Safety and Efficiency
-

Top 5 Tire Valve Sensors You Should Consider for Optimal Performance
-

2025 Top Tire Valve Sensor Innovations You Need to Know
-

Top 10 Benefits of Tire Pressure Sensors for Safe Driving
